Stolen art
Nazis as thieves

-

Leipzig
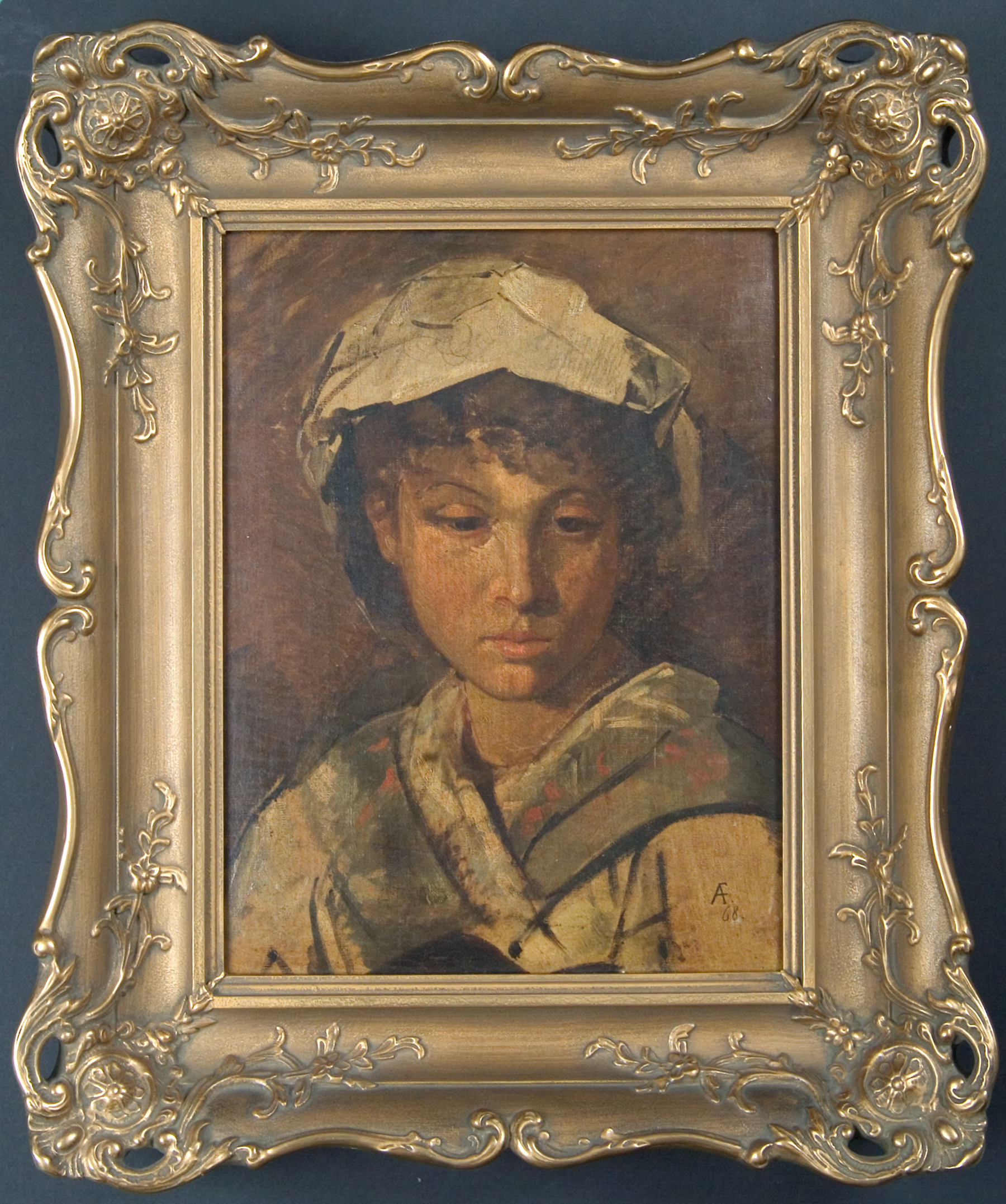
Jewish furriers began to do business at the Leipzig Trade Fair in the middle of the 16th century. For hundreds of years, Jewish traders were allowed into Leipzig only during the fair, but even so, they significantly contributed to the city’s wealth. In the wake of the legal equalization of the Jews in the 19th century, Jewish furriers began to settle in Leipzig, concentrating on a street known as Brühl. Over time, Jews helped to turn the city into an international center of the fur trade. After 1933, many Jewish furriers fled to centers of the trade abroad. Siegmund Fein, born in Leipzig in 1880, was still in Leipzig in 1938. His and his wife’s ordeal under the Nazis culminated during the November pogroms. Siegmund Fein was incarcerated at the Buchenwald concentration camp from November 11th to 30th and badly maltreated. After his release, he was refused appropriate medical care. On December 20th, he fled to Brussels. The painting displayed here, “Head of a Girl” by the German classicist painter Anselm Feuerbach was confiscated by the Nazis – along with other works of art from the Feins’ collection.
SOURCE
Institution:
Leo Baeck Institute – New York | Berlin

Collection:
Anselm Friedrich Feuerbach, Portrait of a Young Italian Woman, in Fein Family Collection, AR 25171

Original:
2004.27